On-line Learning
This section will explain: the operations of label and the best work-flow.
Background
Once your agent is "onboarded", an important question is how to continuously optimize its knowledge base and make itself "smarter". Here, developers need to educate the agent with real conversations recorded after it goes live.
Then our business operations people are the agent's teachers, and after the agent has given its answers, the responses to those responses are first graded for the agent's responses, and then the agent is asked to revise those wrong questions.
The main agent education workplace is on the 'Optimize - On-line Learning' page.
The process of judging here is annotation, which is mainly operated in the to-be-annotated interface; having the agent revise the wrong questions is to add the wrong questions to the agent's knowledge, i.e., adding the revised results to the intent trigger, and working on the review page.
Operating instructions
Clicking on the "Filter" button expands the relevant filter criteria and allows you to select the source of processing as "log statement" or "re-tag".
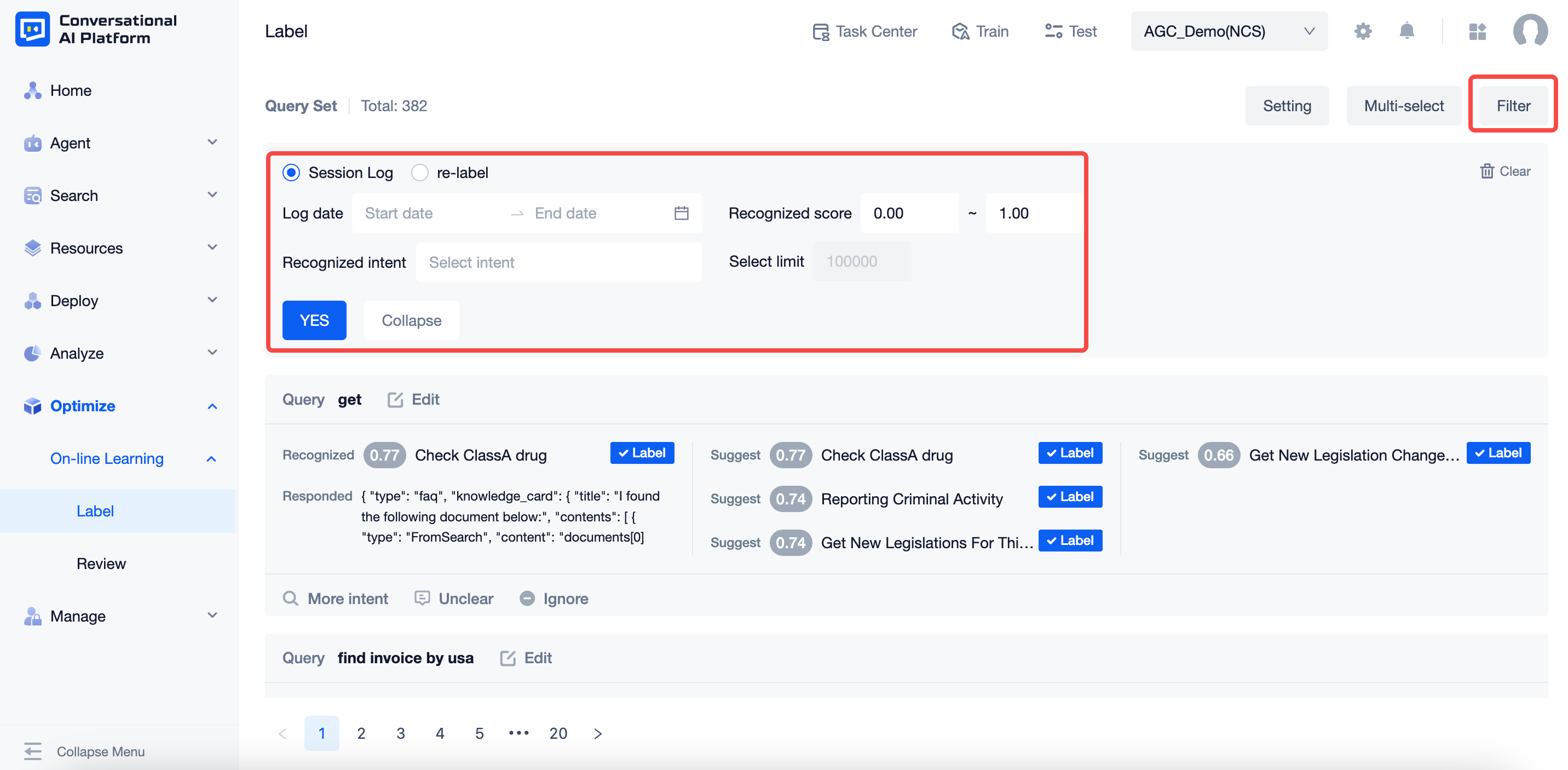
Log statements: unmarked data, not including "agent test" data
Relabeling: in the marked page is knocked back to the section that needs to be reworked and relabeled, similar issues that are already in the intent will not appear here.
Filter fields and field values:
- Source of the corpus to be annotated: "Log statement" or "Re-label", single choice only
- The query time is the corresponding time period, for example, "2021-09-12 → 2021-09-15", and you can select a date range.
- Identify intent fractional places between 0 and 1, up to two decimal places, e.g. "0.5 ~ 0.85".
- Identify the intent with the option to select multiple intents or a single intent, with no intent.
- The maximum number of corpus is 100,000, which cannot be modified. After exceeding the number of reviews, the earlier ones will be deleted automatically according to the chronological order.
Operation interaction logic
- Filtering: When you click the "Filter" button, the filter box will be displayed.
- If no filtering has been performed, click the "Filter" button to expand the filter box
- If the filter box is already displayed, click the "Filter" button, the filter box remains and is not put away
- If the filtering operation has been performed, when you click the "Filter" button, the filtering conditions displayed in the filter box are the current filtering conditions
- Record the current user's history of filtering criteria for this agent, and as long as it is not cleared, the previous filtering criteria will remain when the current page is accessed again
- Yes: After setting the filtering conditions, click the "Yes" button to filter and display according to the newly set filtering conditions.
- Collapse: after setting the filter criteria, click the "Collapse" button, the filter box is Collapsed, the page remains unchanged; click the filter again, the filter criteria before "Collapse" is still displayed
- Clear: Click Clear to clear the filtering conditions and the page will return to its unfiltered state.
- Filtering: When you click the "Filter" button, the filter box will be displayed.
The main operations of the annotation card page, displayed in the list of statements to be annotated, in ascending order of time.Card contents include:
- User statement: the real statement sent by the user, you can edit the user statement, also support editing as a sentence, the edited statement will overwrite the original statement directly, can not be modified to empty.
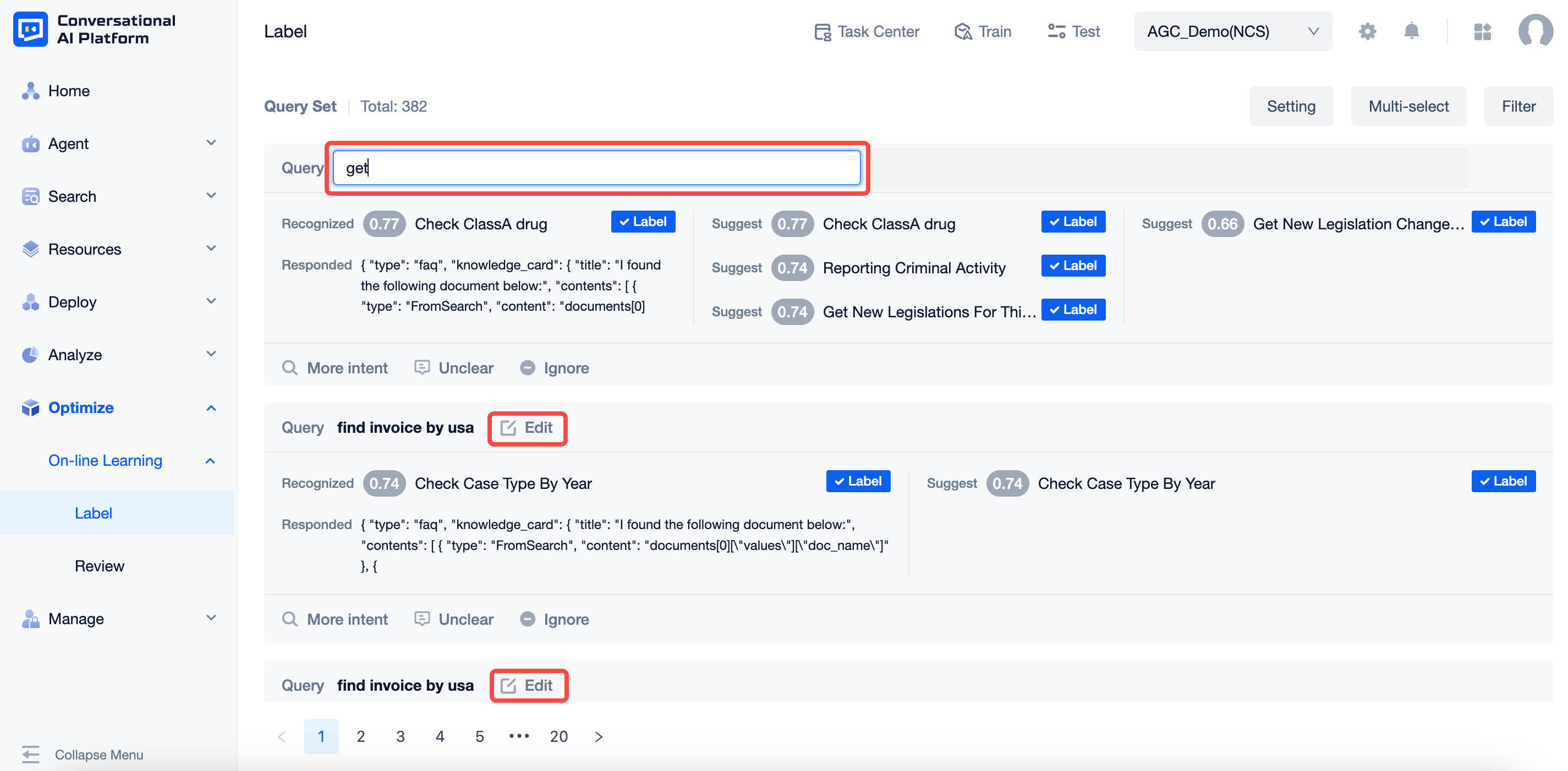
- Identify intent: the intent identified and scored by the agent in the real log, or the intent name "-" if it is a tout
- Reply to: Show the first reply to the real log
- Recommended intent: the intent that is recommended up to top6 based on the current agent status (meaning the intent with the higher recognition intent score among the intents other than the recognition intent)
- Clicking on an intent name brings up the intent details editor for viewing details and making related changes.
- Label: The corresponding intent is Labeled as the correct intent, and the current statement goes to the Labeled review page when clicked.
- Other Intentions: click on the pop-up window to display a list of Intention names, support search for Intention names (including custom Intentions and preset system Intentions) or new Intentions, after selection, you also need to indicate whether it is an in-bank issue and an out-of-bank issue.
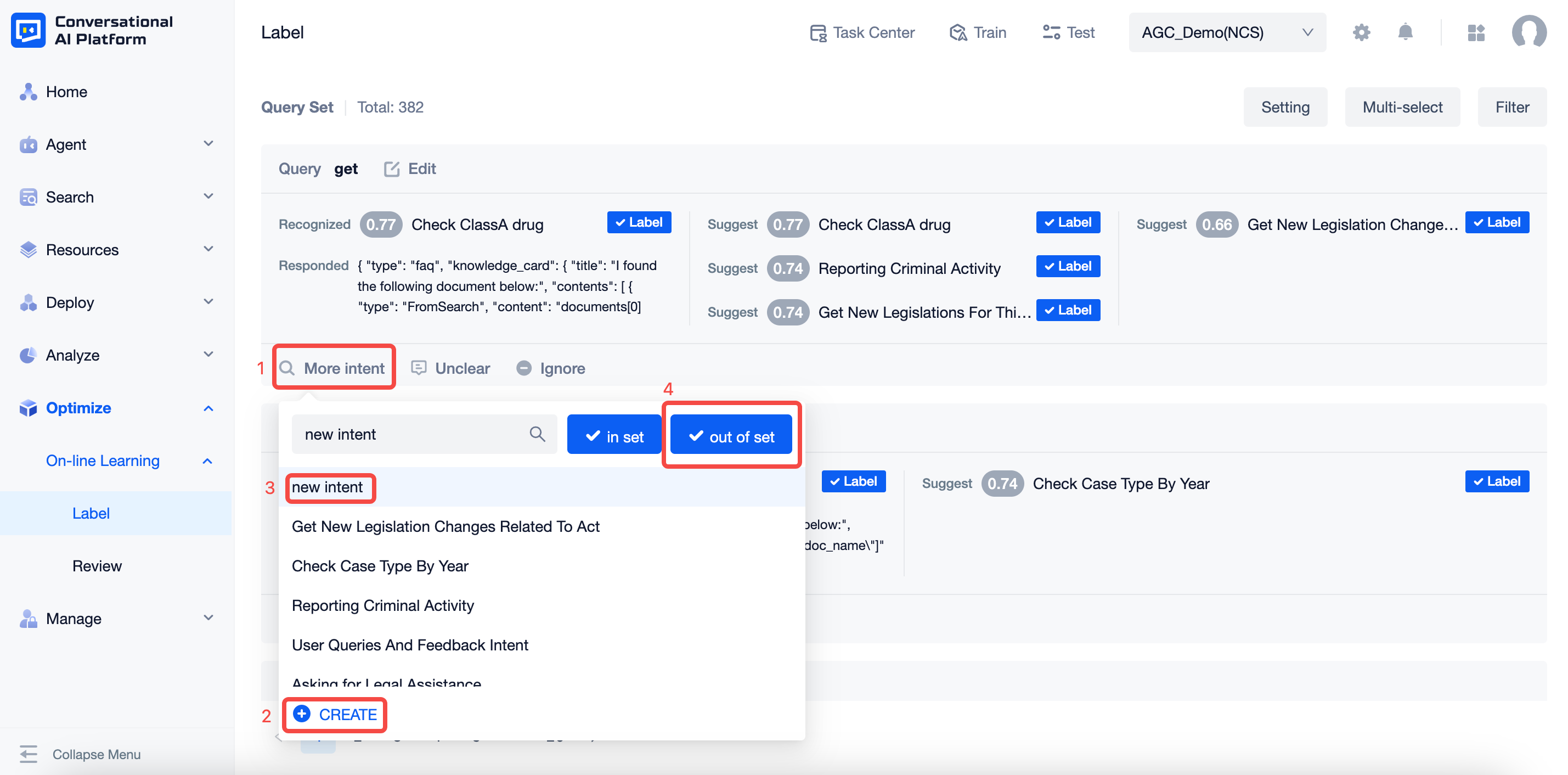
- New Intent: When you click on it, you can add a new corresponding intent, which is mainly used when the user statement is business knowledge but there is no corresponding intent in the agent, then you need to create a new one.
If it is found that the user's utterance should belong to an intent that has not yet been created in the agent, or an intent that was created later than this message, a new intent should be created or the corresponding new intent should be selected and marked as out-of-bank, since the agent does not have the relevant knowledge when the message enters the agent.
- Semantic uncertainty: click on it and the current statement disappears, entering the annotated data, usually used when the user enters meaningless words, expressions, symbols, pure alphanumerics, etc.
- Ignore: click on the current statement to disappear and enter the annotated data, usually used for one-time processing questions, where the user's question is specific and will not reappear in the foreseeable future based on experience
Batch processing: you can batch select the current page of the content to be marked up for marking semantic unknown, ignore, and the intention to identify the correct results; the page can click to cancel the batch processing operation.

Settings: you can check the recall intent that does not match the annotation intent after annotation, i.e., the agent recalls the wrong one quickly added to the intent trigger.

note
Intent-triggered validation requires clicking on Validate and "Train and Publish" to train and publish the agent.
Workflow proposals
For more efficient agent-critiquing and education, here are some suggestions for handling the more mature agents in separate categories. User statements can be classified into three types according to their confidence level:
A high confidence user claim. This means that the agent has recognized this user sayings accurately. It also means that the agent does not need to learn these user claims any more.
Medium confidence user claim. This means that the agent is not so sure about this user claim and needs to be "educated" by the developer.
Low-confidence user claims. This means that the agent is unfamiliar with this user claim, and at this point, it is likely that such user claims represent intentions that are not in the agent's existing knowledge system.
Accordingly, you can use the filtering on the annotation page to perform the relevant processing, and you can set the recognition intent score interval for this batch of processing by yourself to help your annotation work more quickly.
- low score quick exclusion, you can filter set 0.00-0.01 score interval segment, batch mark which expressions, symbols, letters, links and other cases as semantic unclear.
- High Score Extreme Confirmation, you can filter to set the score range of 0.90-1.00, because this part of the score is extremely high, so you can quickly browse the intention of positive and incorrect batch confirmation.
- The next highest score band is treated progressively, either in intervals of 0.1 or 0.05 downwards, for example (0.8-0.9 → 0.7-0.8 → 0.6-0.7).
- When dealing with user statements with low agent response scores, a new page can be opened for search intent, which helps improve efficiency.