Queues
Queues
Queues is used to view and manage the related contents of RPA process calls. You can create a queues here so that the Creator or Worker can write data to the queues or get data from the queues, thus realizing the information transfer function.
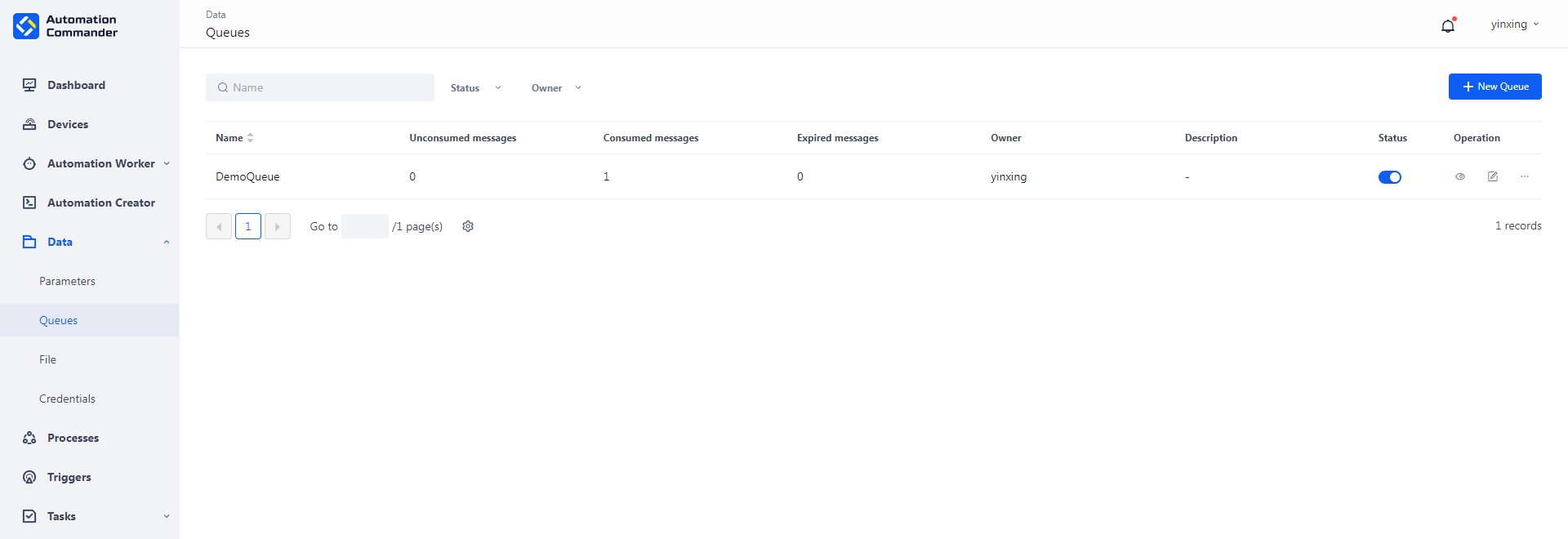
New
To create a new queues, click the "New queues" button, fill in the name and description of the queues, and then save it. Please note that the queues name cannot be the same as other existing queues names, otherwise the system will prompt that "the same queue name already exists".
Tip: You can only view queues within your permission range, but when you create a new queues, the system will check whether the queues name is the same as all queues. Therefore, it may have the same name as other queues that are not visible to you.
Add collaborator
Select the queues that needs permission control in the queues list, and click the "Add collaborator" button to set the corresponding collaborator permissions.
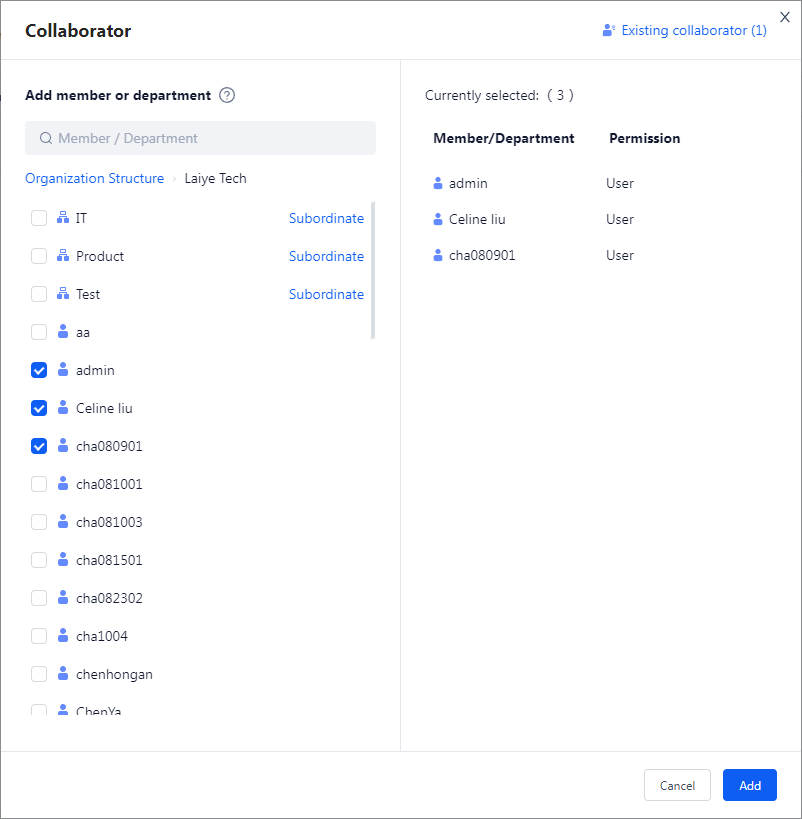
| role name | Instructions |
|---|---|
| User | Users who can use the queues in task. |
View queues - queues Information
Click View queues to view the basic information of queues.

| role name | Character Description |
|---|---|
| owner | You can edit, delete and Add collaborator to the queues, and the owner's permission can be transferred |
| manager | You can edit the queues, Add collaborator, view and use the queues in task, and operate on and off status |
| editor | Only the queues can be edited, viewed, and used in task. The queues can be opened and closed |
| User | You can only view and use the queues in task, and you can operate the menu of queues messages |
View queues - Message Content
By clicking the "View More" button (the small eye icon on the right), you can view the message records in the queues, including the following information:
- Message Number: A unique identifier automatically generated by the program, used to mark a message.
- Message Source: the initiator of the message queue, that is, the initiator of the task generating this message.
- Queuing time: the time when the message was added to the queues.
- Effective time: The effective time of the message.
- Expiration time: The expiration time of the message.
- Priority: The consumption priority of messages, divided into high, medium, and low.
- Consumer: the consumer of the message, that is, the initiator of the task consuming the message; If it is a manual consumption, it will be displayed as a manually operated user.
- Status: The current state of the message.
The message status includes the following four types:
- Not effective: The message has not reached the effective time and cannot be consumed.
- Not consumed, effective: The message has reached the effective time and can be consumed.
- Consumed: The message has been obtained from queues by Worker, and other Worker cannot obtain the message again.
- Invalid: The message has exceeded its expiration time and cannot be consumed.
The sources and consumers of information include the following four types:
- Creator: When developing an RPA process on the client side, the Creator puts the message content into a queues or takes it out of a queues through the "Put in queues" or "Take out queues" command.
- Worker: when the Floating License Worker or Unattended Worker runs the process, it will write the message content to the designated queues according to the "Put in queues" command in the process; According to the "Get queues" command, the message content is read from the queues.
- OpenAPI: The third party application uses the OpenAPI interface to write the message content to the queues or get it from the queues through the application authorization of the Commander.
- Specific user name: When a user manually performs queue or consumption operations, the source and consumer of the message will be displayed as the user's name.
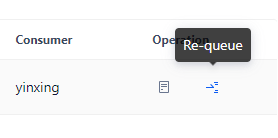
Re-enqueue
Click the "Requeue" button to rejoin the consumed messages to the queues. In this window, users can edit the message content. The news of rejoining the team will be considered as a new message.
Edit
To modify the queues information, click the "Edit" button to edit the name and description of the queues.
Note: Modifying the name of a queues may cause the historical process to fail to correctly reference the queues, which may result in task errors. Please operate with caution.
Delete
To delete a queues, click the "Delete" button in the list. After the second confirmation, the system will delete the corresponding queues.
Note: Deleting a queues may cause historical process to fail to correctly reference queues, which may result in task errors. Please operate with caution.